Level: Beginner
In this article we explain what Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and Voice over IP (VoIP) are, how they work, the advantages and disadvantages of VoIP, what you need to use VoIP, and the types of IP phones available.
1. IP TELEPHONY: WHAT IT IS
IP telephony is a telephony that uses an Internet connection to make and receive calls. Today, in 2023, almost all businesses and individuals use VoIP.

With VoIP, calls can be made from various devices connected to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) over the Internet to traditional phone numbers and also have a phone number.
2. IP TELEPHONY: WHAT IT DOES
IP telephony or ToIP (Telephony over Internet Protocol) is telephony where the voice signal is sent in the form of data packets over the Internet (Voice over IP) or a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
It uses the Internet Protocol, hence the abbreviation IP. VoIP operators are also interconnected with the traditional telephone network to enable communication between VoIP users and traditional telephony subscribers.
This interconnection with the traditional telephone network allows calls to be made to traditional telephone numbers, such as geographical numbers, mobile numbers, nomadic numbers and/or special rate numbers (902, 900, 800…); and to have a geographical number that any user can call.
IP telephony is based on Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology, which converts voice into data packets so that they can be sent over the Internet.
Find out more about Voice over IP on Wikipedia
3. IP TELEPHONY AND VOICE OVER IP: DIFFERENCES
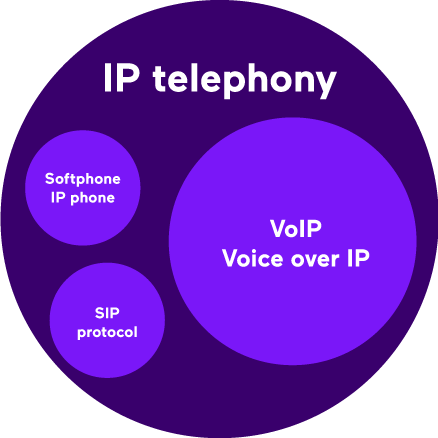
The main difference between IP telephony and Voice over IP is that one refers to the communication system and technology used, and the other refers to the technology used to send the voice:
- IP telephony: is the communication system that allows telephone conversations (between different telephone numbers) using VoIP, i.e. over the Internet.
- Voice over IP or VoIP: is the set of resources that allow the voice to be sent over the Internet. We could talk about VoIP technology.
VoIP would not exist without Voice over IP, as it is the basis of its operation.
4. HOW DOES IP TELEPHONY WORK?
By default, voice is analogue, and operators convert this analogue signal into data packets so that they can be sent over the Internet. These packets are then decompressed to be heard by the person at the other end of the line. And, of course, this happens in the blink of an eye.
Compression and decompression also occur when the call changes channel, for example, when an Internet call is routed through a switch to an operator using a cable system.

1. The VoIP user dials the phone number of another traditional phone user.
2. The VoIP operator connects to the PSTN and connects to User B’s number. The call is connected at both ends regardless of the technology used.

3. User B answers the call. The voice is sent over frequencies through the telephone network.
4. The voice arrives at User A’s VoIP operator, which converts it into data packets.

5. The voice is decompressed when it reaches User A’s device to hear User B.
6. User A speaks and the device compresses the voice into data packets.
7. The data packets are sent over the Internet until they connect to the telephone network.
8. The data packets are decompressed so that they can travel through the telephone network and arrive at User B in the form of voice.
5. WHAT YOU NEED FOR VOIP
To use VoIP in your business, you need to meet three requirements:
- Use the services of a VoIP operator
- Have an Internet connection
- Have a telephone or device to make calls
5.1 PARTNER WITH A VOIP OPERATOR
To use VoIP, you need to subscribe to the services of a VoIP operator: they will provide you with a line and connect you to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) to contact other telephone users.
The VoIP provider will also offer telephone numbering, a virtual PBX, customer service software, telemarketing software and more.
5.2 INTERNET CONNECTION
With VoIP, voice is sent over the Internet, so it is essential to be connected to the network.
The type of connection does not matter as long as it meets minimum quality requirements such as bandwidth, continuity or jitter.
VoIP works with the following types of Internet connections:
- ADSL
- WiFi
- Cable
- Fibre
- Satellite (variable quality, not recommended)
- WiMAX (variable quality, not recommended)
- 5G
- 4G
- 3G (variable quality, not recommended)
5.3 TERMINALS FOR dialing AND RECEIVING VOIP CALLS (SIP CLIENTS)
In VoIP we talk about terminals, devices or SIP clients because, unlike conventional telephony, mobile phones, computers and tablets can be used to make calls in addition to telephones.
Because the voice signal in VoIP is sent over the Internet, you need a device that is connected to the network.
IP phone

An IP phone is a phone designed specifically for Voice over IP (VoIP) technology. Unlike analogue phones, IP phones are mini-computers, which means they have built-in software and connect to the Internet. In fact, to set them up, you need to use a computer and access the IP phone’s software.
IP ATA adapter
The IP adapter, or ATA adapter, is a device that allows regular telephones to be used with VoIP. This adapter converts the signal from analogue phones into data packets and vice versa. Simply connect it to the phone and then to the router so that the phone can work with the Internet.
It is important to note that these adapters are becoming increasingly obsolete as communication is limited to the functionality of traditional phones.
Softphone
A softphone is software that emulates a telephone and can be installed on computers, smartphones and tablets to make VoIP calls.
6. VOIP VS. TRADITIONAL TELEPHONY
VoIP and traditional telephony serve the same purpose: to enable communication between two people in different locations. The difference between the two lies in the channel through which the communication takes place, but also in their requirements and characteristics.
Each telephony system has its advantages and disadvantages. A few years ago, it was suggested that the disadvantage of VoIP was poor call quality, but as network speeds have improved, this is no longer an issue. With 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, ADSL, fibre, etc., we have more bandwidth, more stability and lower latency. The Internet is now ready for VoIP.

7. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF VOIP
IP telephony has many advantages, but there are also some disadvantages.
7.1 MAIN ADVANTAGES OF VOIP
Cost savings
With IP telephony, savings are particularly high in business environments, where a company with 100 lines could save up to €1000 per month.
Mobility
Unlike traditional telephony, VoIP allows you to use a fixed line number from anywhere with an Internet connection. At a business level, this has been a great solution during COVID, allowing the extension and office line to be used when working from home.
Features and functions
With VoIP, the list of features and capabilities is incredible and continues to grow. Like any software that updates and offers more options, VoIP is constantly improving.
The clearest example is a virtual PBX, which have reached the point where a virtual PBX can integrate with CRMs and communication channels such as WhatsApp or email in the same environment. This is unthinkable with analogue telephony.
7.2 DISADVANTAGES OF VOIP
The main disadvantage of IP telephony is that you need an Internet connection to use it. A few years ago, this was a significant disadvantage because internet connections were much slower, so call quality was not ideal.
Today, this is no longer a disadvantage because every business has a good internet connection and if the internet goes down, the phone is likely to be the least of that business’s problems until the connection is restored.
IMPORTANT: the connectivity of the VoIP service also depends on the VoIP operator, so it is advisable to sign up with a stable operator.
8. PORTING A NUMBER TO VOIP
Porting a fixed line number to VoIP is the same as porting to any traditional telephone operator. You will need to subscribe to the services of a VoIP operator and request number portability.
Your new Voice over IP telephone provider will be responsible for managing the migration of your number to the new system. And if you later decide to go back to analogue telephony, you can also reverse the process and port your number to a traditional telephone operator.
 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Ask for a demo
Ask for a demo

 6 min
6 min
